Are You Experiencing Gallbladder Issues?
What is Gallbladder Disease?
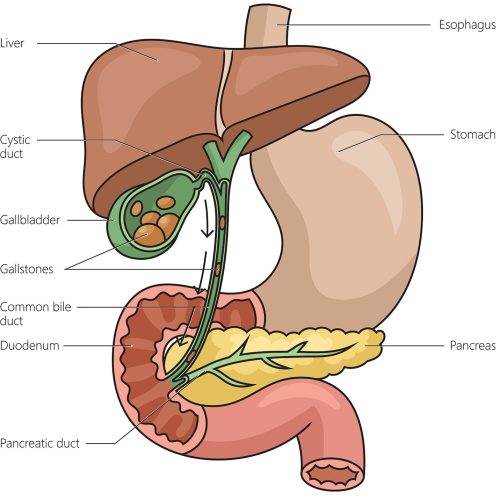
Gallbladder disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the gallbladder, a small pear shaped organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder is an expendable organ which usually functions by stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver.
Common types of gallbladder disease
Hardened deposits of bile that can form in the gallbladder. They may cause pain, infection, or blockages in the bile ducts.
Biliary colic is a type of pain that occurs when a gallstone temporarily blocks the bile duct, causing a buildup of bile and increased pressure in the gallbladder. This condition is also known as a gallbladder attack and typically lasts from a few minutes to several hours.
This is the continuation of biliary colic where symptoms do not subside and are persistent.
The most common cause of cholecystitis is unrelenting blockage of the gallbladder outlet due to gallstones which leads to inflammation of the gallbladder.
Acute cholecystitis is a serious problem and requires urgent surgical treatment. Gangrenous cholecystitis (or a dead gallbladder) can set in if the gallbladder obstruction is not resolved. This in turn can result in gallbladder wall perforation and leakage of gallbladder contents into the abdominal space, causing peritonitis.
Chronic cholecystitis is less common. It is long-term gallbladder inflammation due to repeated episodes of acute cholecystitis or persistent irritation from gallstones
Remember to seek urgent medical help if gallbladder pains persiste for more than a day
Rarely, gallstones can migrate from the gallbladder into the common bile duct where it can cause bile duct obstruction. Patients tend to experience typical symptoms of jaundice (yellowness in their eyes), right upper abdominal pain.
In the worse case scenario, bile duct infection (i.e. Cholangitis) can occur which is a medical emergency.
There are many causes to pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
2 of the most common causes (making up 90% of cases) are:
- Gallstones
- Excessive alcohol intake
Severe pancreatitis is again a surgical emergency as it can be life-threatening.
Growths or lesions that form on the gallbladder wall. While most polyps are benign, some may need to be monitored or removed if they are large (greater than 1cm) or cause symptoms.
We tend to recommend surgery for larger polyps as there is an increased risk of gallbladder cancer transformation (i.e. 5% if polyps are greater than 1cm, 15% if polyps are greater than 1.5cm).
A condition where the gallbladder is dysfunctional and does not empty bile properly, leading to biliary colic (pain). This condition is independent of gallstones.
A rare but aggressive form of cancer that begins in the gallbladder
What are Gallstones?
Gallstones are solid particles that form in the gallbladder from bile cholesterol and bilirubin. They can vary in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball and can cause pain, infection, or blockages in the biliary tract.
Types of Gallstones
Cholesterol Gallstones:
- The most common type, accounting for about 80% of gallstones.
- Formed primarily from hardened cholesterol.
- Yellow-green in color.
Pigment Gallstones:
- Formed from excess bilirubin.
- Smaller and darker than cholesterol stones, often brown or black.
- Associated with conditions that cause increased breakdown of red blood cells, such as hemolytic anemia or liver cirrhosis.
- Mixed gallstones:
- in some cases, a mix of both type of stones are present.
Causes of Gallstones
The exact cause of gallstones is not clear. However, gallstones can form due to an imbalance of cholesterol and bilirubin; or inadequate emptying of the gallbladder.
The risk factors that increase the chance of having gallstones include:
- Pregnant women and women taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy
- Age (>50 years old)
- Genetic factors & family history of gallstones
- Ethnic background, esp. native Americans and South Americans
- Obesity
- Rapid weight loss
- Use of cholesterol-lowering drugs
What Are Common Gallbladder Symptoms?
Gallstones do not always cause symptoms, and are sometimes called ‘silent stones’. In fact, within our population, 20% of people have gallstones without even knowing it. These are often incidentally found when your physician is investigating you for another problem.
Here are some of the symptoms which you may have experienced:
- Upper abdominal discomfort, pain lasting for several hours before subsiding
- Usually following a fatty meal
- Usually in the evening or early hours of the morning
- Bloating
- Increased heartburn or reflux
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shoulder blade or back pain
- Jaundice (yellowness of the skin or eyes) suggests gallstone blockage of the bile duct
- Accompanying high grade fevers or chills
- Unrelenting pain which suggests cholecystitis
- Unrelenting pain in the back which suggests pancreatitis
How Do We Diagnose Gallbladder Disease?
Dr Cheng will help diagnose your gallbladder issues based on:
- your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination.
- Confirming them through dedicated imaging studies such as:
- Ultrasound (most common)
- CT/MRI imaging is rarely needed
- HIDA Scan may be required to rule out dysfunctional gallbladders in the abscence of stones
How Do We Manage Gallbladder Disease?
Gallstones without symptoms do not require treatment.
The “GOLD STANDARD” Treatment for symptomatic gallstones and its complications includes surgery to remove the gall bladder (cholecystectomy). Gallbladder surgery is almost always performed through keyhole surgery.
Rarely, medications like Ursodiol can help dissolve small gallstones/ gravel but this process may take several months to years. As such, this option is reserved only for patients contraindicated to surgery.



